Engineering or Apprenticeship Programs
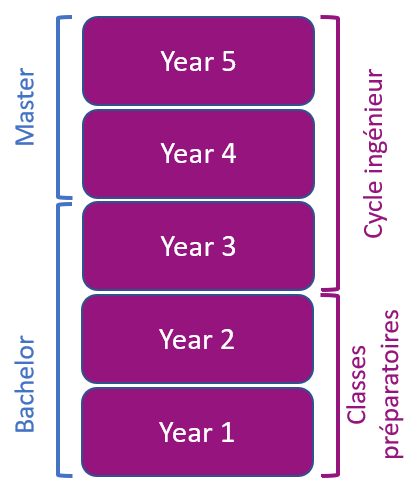
The engineering program can be completed as a student or apprentice. Only the final year is the same for both paths.
During the first two years of the engineering program, students will gain a solid foundation in Computer Science, Networking, Electronics, Embedded Systems, Automation, Cybersecurity, and Artificial Intelligence. They will also have the opportunity to choose elective modules that will prepare them for the specializations in the final year.
In the second year of the engineering program, students and apprentices begin to specialize, with at least 50% of their courses being electives.
By the fifth year, they are required to choose one of four specialties. Additionally, they can take elective modules to deepen their knowledge in their chosen specialty or broaden their knowledge in other fields.
Throughout the engineering program, there is a strong emphasis on practical learning. This includes engaging in school projects, internships at companies, or participating in the school-company work-study program in collaboration with ITII Dauphiné-Vivarais.
At Esisar, students are required to have international experience (whether for academic purposes or internships).
Students must spend at least one semester abroad (17 to 20 weeks).
Apprentices must spend at least one term abroad (9 to 12 weeks).
During their studies, students are required to learn modern languages, with English being compulsory and other languages being optional. They also receive instruction in sports, business techniques (including business knowledge, project management, eco-design, entrepreneurship, innovation, and creativity), societal issues (such as sustainable development and social responsibility), and research.
In addition, students take courses related to personal development (self-knowledge and professional projects).
During the first two years of the engineering program, students will gain a solid foundation in Computer Science, Networking, Electronics, Embedded Systems, Automation, Cybersecurity, and Artificial Intelligence. They will also have the opportunity to choose elective modules that will prepare them for the specializations in the final year.
In the second year of the engineering program, students and apprentices begin to specialize, with at least 50% of their courses being electives.
By the fifth year, they are required to choose one of four specialties. Additionally, they can take elective modules to deepen their knowledge in their chosen specialty or broaden their knowledge in other fields.
Throughout the engineering program, there is a strong emphasis on practical learning. This includes engaging in school projects, internships at companies, or participating in the school-company work-study program in collaboration with ITII Dauphiné-Vivarais.
At Esisar, students are required to have international experience (whether for academic purposes or internships).
Students must spend at least one semester abroad (17 to 20 weeks).
Apprentices must spend at least one term abroad (9 to 12 weeks).
During their studies, students are required to learn modern languages, with English being compulsory and other languages being optional. They also receive instruction in sports, business techniques (including business knowledge, project management, eco-design, entrepreneurship, innovation, and creativity), societal issues (such as sustainable development and social responsibility), and research.
In addition, students take courses related to personal development (self-knowledge and professional projects).
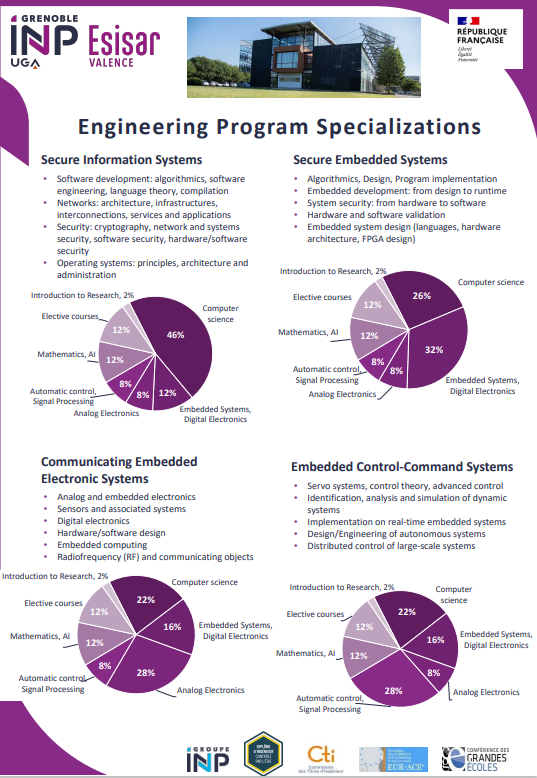
Specializations proposed at Esisar
Secure Information Systems (SIS)
Software and application development (business, embedded, web). Networks. Network and systems security. Operating systems. Artificial Intelligence.
Secure Embedded Systems (SES)

Embedded development: from design to runtime (languages, hardware
architecture, FPGA design). System security: from hardware to software. Hardware and software validation.
Communicating Embedded Electronic Systems (SEC)
Analog and embedded electronics. Sensors and associated systems. Hardware/software design. Embedded computing. Radiofrequency (RF) and communicating objects.
Embedded Control-Command Systems (S2C)

Advanced Control. Identification, analysis and simulation of dynamic
systems. Implementation on embedded systems. Design/Engineering of autonomous systems. Distributed control of large-scale systems
And 3 complementary areas of expertise
Intelligent Distributed Systems

Cybersecurity of Hardware and/ or Software Systems

Radiofrequency Systems

French State controlled diploma conferring a Master's degree

What is a grande école ?
French engineering curriculum