Our Engineering degree at Esisar

The elite degree in technology
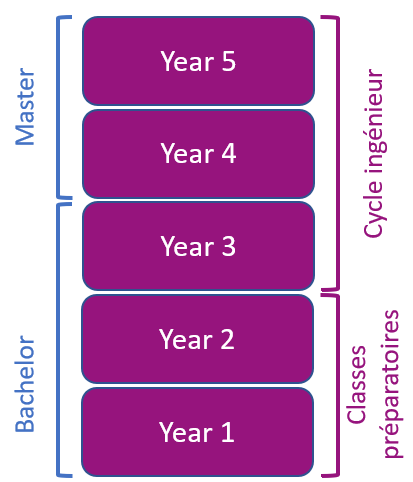
In France, there is a distinction between university and Engineering School. The latter are open to excellent students through selective entrance. The engineering degree is recognized as a master's degree overseas and can lead directly to PhD studies. Most students carry out preparatory classes (Year 1 and Year 2) where they receive intensive training in mathematics and physics before entering an Engineering university (Year 3 to Year 5) through a selective exam.
Upon completing Year 5, students are awarded their Engineering degree, which is recognized as a master' degree globally.
2 specializations
- Embedded Systems: electronics, computer sciences and control (EIS specialization in French)
- Information Technology & Security (IT&S): computer sciences, networks and security (IR&C specialization in French)
5 year integrated engineering curriculum
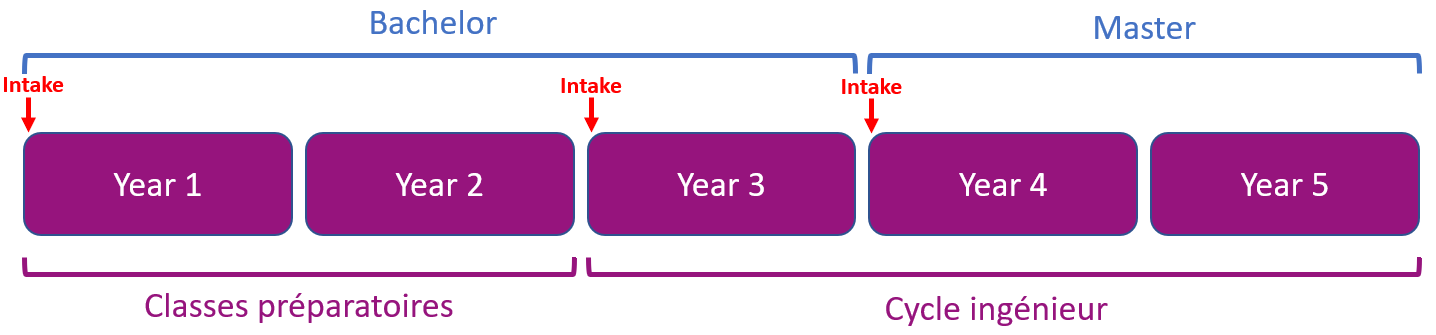
Many engineering universities in France provide an engineering curriculum from Year 3 to Year 5 only. At Esisar, you will have the opportunity to study both preparatory courses and the engineering curriculum. Students can either start their degree at Year 1, Year 3 or Year 4.
The curriculum at ESISAR is built into two cycles:
The preparatory cycle (2 years): theoretical courses and labs, to learn basic scientific knowledge and discover engineering sciences.
The Engineer cycle (3 years). The first year consists in common core courses, which allows the student to reach a “bachelor” level in engineering sciences.
100% international experience
Nowadays engineers work on global issues within multicultural companies. Hence they need to acquire intercultural skills and international experience to be able to work in international teams and build their resilience in a fast pace and constant change environment. Engineering students at Esisar are then required to have this international experience in order to graduate.
1 year of industrial experience
During the first year of the Engineer cycle, the Students have to make a 6-weeks technician internship. In second year, they lead a 6-months Industrial Project in direct relationship with Companies. In third year, they carry out the Final Year Project: a 5-months internship in a company that ends the curriculum.
100% job placement in 6 months
What is a grande école ?
French engineering curriculum